What are the differences between a human resources system and an attendance and payroll system, and how are they defined?
-
-
InfoDetail_Editor: Tony
-
1089
- Wx Share
-
-
-

Time & Payroll Suite
Attendance, Payroll and Access Control Solution for Cost Reduction and Productivity Gains Details
All‑in‑one automated timekeeping and payroll system with robust, secure processes to guarantee payroll integrity. Includes leave management, shift rostering, multi‑site and chain support, multi‑ledger accounting, and comprehensive modules.
Differences and Definitions Between Human Resource Management Systems and Attendance and Payroll Systems
Introduction
In modern enterprise management, human resource (HR) related software systems play a crucial role. However, the commonly available "Human Resource Management System" (HRMS) and specialized "Attendance and Payroll Systems" are often confused, leading to misunderstandings when companies select and implement them. This article will delve into the core differences, functional scope, and defining criteria of the two, and use DGX HRMS as an example to illustrate how a system focused on "on-the-job employee management" can position itself within this spectrum, assisting companies in making informed technology investment decisions based on their own needs.
Main Body
I. Core Definitions and Scope Differences
Essentially, a Human Resource Management System (HRMS) is an integrated platform covering the "full lifecycle" management of employees. Its scope is broad, typically including:
Recruitment and Hiring: Job posting, resume management, interview scheduling, talent pool building.
Employee Information Management: Personal basic information, contracts, career history, skills certifications.
Training and Development: Course management, training planning, performance appraisal, and career path planning.
Core HR Administration: Organizational structure, job grades, transfer and departure processes.
The Attendance and Payroll System is an important subset or specialized module of an HRMS, with its core tasks highly focused on:
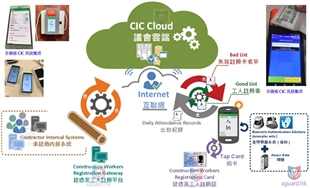
Attendance Management: Clocking in and out, leave requests, overtime, and business trip reporting.
Complex Calculations: Accurately calculating working hours and various allowances based on scheduling rules, leave policies, and labor laws.
Payroll Calculation: Integrating attendance results, tax settings, social security contributions, and various rewards and penalties to automatically generate accurate payroll.
In short, an HRMS focuses on the entire journey and development of an employee from potential talent to departure; while the attendance and payroll system deeply focuses on the two most core and compliant operational data points during an employee's employment: "time" and "money."
II. Functional Focus and Complexity Analysis
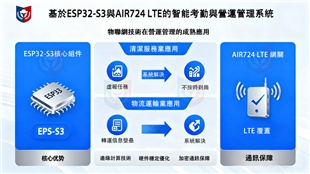
Traditionally, many comprehensive HRMS systems include attendance and payroll as a built-in function. However, for industries with complex workforce structures (such as multi-shift systems, flexible working hours, and cross-regional operations) or extremely high regulatory compliance requirements (such as manufacturing, retail, and service industries), general-purpose modules often cannot meet their in-depth needs.
Take DGX HRMS Attendance and Payroll System as an example. Although categorized under HRMS, its core design and market entry point clearly focus on in-depth management "after becoming an employee", particularly in the complexity of attendance calculation. This perfectly reflects the positioning of a type of specialized system in the market: they are not all-encompassing, but rather excel in key processes.
The complexity in the attendance field is mainly reflected in two modules:
- Schedule Management:
Requires handling various systems such as regular day shifts, rotating shifts, flexible working hours, and variable working hours.
Requires considering regulatory restrictions such as shift handover, rest intervals, and legal working hour limits.
The system must be able to adjust shifts, substitute shifts, and schedule temporary shifts according to business needs, and synchronize these changes to the payroll calculation logic in real time.
- Leave Management:
Multiple types of leave (special leave, sick leave, personal leave, maternity leave, parental leave, etc.) must be defined, each with potentially different pay rules and documentation requirements.
The system must automatically calculate and update the number of special leave days based on seniority.
The system must handle the entire process of leave application, approval, and cancellation, ensuring the real-time accuracy of remaining leave days.
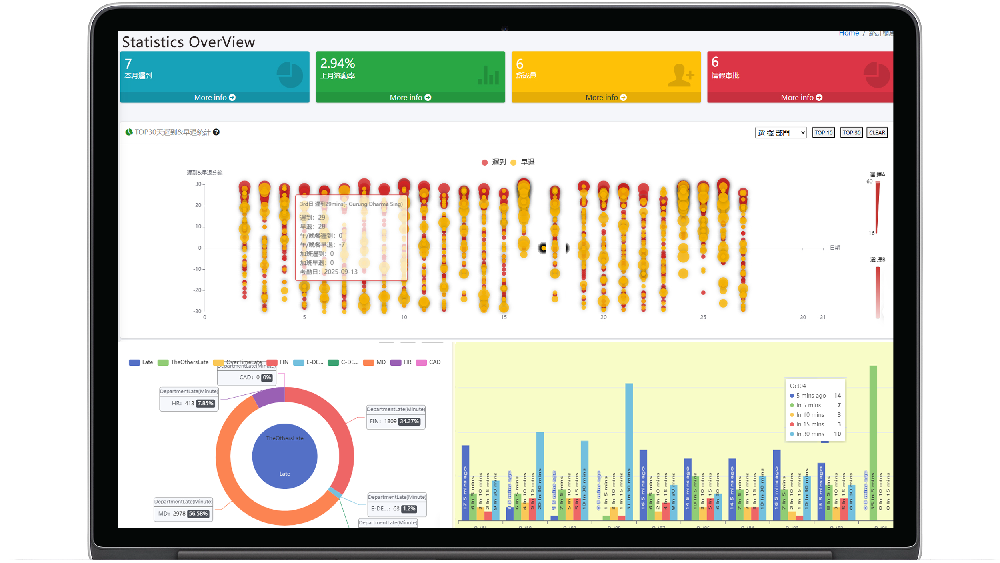
The data from these two modules intertwines to form the foundation of payroll calculation. Any exceptions or errors in the rules will directly lead to payroll calculation errors, causing employee disputes and compliance risks. Therefore, a robust attendance and payroll system must possess highly flexible and accurate algorithms and rule engines.
III. How to Define and Select a System: Enterprise Needs-Oriented
When differentiating and selecting a system, enterprises should return to their own management pain points and strategic goals:
Situations for Choosing a Comprehensive HRMS:
The enterprise is in a rapid growth phase and needs to systematically manage the entire process from recruitment to termination.
The most pressing needs are to improve recruitment efficiency, integrate employee data, or establish a standardized training and performance system.
Employee shifts are simple, and attendance and payroll rules are relatively straightforward; the standard modules of a comprehensive system are sufficient.
Situations for Choosing a Professional Attendance and Payroll System (or a system focused on on-the-job management like DGX HRMS):
The core pain points are chaotic scheduling, incorrect time calculations, and delayed or frequently erroneous payroll payments.
Labor-intensive, with complex shifts, and a need to strictly adhere to changing labor regulations (e.g., for different regions).
Other systems (such as recruitment websites and e-learning platforms) already handle the HR front-end processes, but a reliable core computing engine is lacking to process attendance and payroll. * Accurate time data is needed to analyze labor costs and productivity.
The key is understanding: "Functionally similar" only refers to similar module names; the underlying depth of business logic, computing power, handling of compliance details, and fit with specific industry processes are the key differentiators of system quality and applicability. DGX HRMS enters the market with its strengths in "attendance and payroll," targeting companies with a strong need for "accurate calculations" and "compliance automation."
Conclusion
In summary, Human Resource Management Systems (HRMS) and attendance and payroll systems are related as "surface" and "point." Traditional HRMS aims to provide a one-stop, breadth-first solution; while professional attendance and payroll systems (or HRMSs centered around this) pursue depth and ultimate accuracy in key operational processes.
When defining their own needs, companies should not be misled by the classification names of systems, but should conduct in-depth analysis: Does my biggest management challenge currently stem from the selection, training, utilization, and retention processes of "people," or from the calculation and compliance pressures of "time and pay"? For the latter, choosing a system like DGX HRMS, which, while bearing the name HRMS, actually focuses on complex scheduling, leave, and payroll calculations, is often a more direct and effective solution. Clear definition helps companies invest resources in tools that solve core problems, thereby improving management efficiency, reducing compliance risks, and protecting the rights and interests of employees.
Software Service
Industry information
- Views 8944
- Author :Tony
- Views 603
- Author :Tony
- Views 1661
- Author :Bruce Lee
- Views 41
- Author :Tony
- Views 15
- Author :Bruce Lee
- Views 29
- Author :Tony
































































Hardware & Software Support
We are deeply rooted in Hong Kong’s local services, specializing in hardware and software issues.
System Integration
Hardware and software system integration to enhance stability and reliability.
Technical Support
Professional technical team providing support.
Professional Technical Services
Focused on solving problems with cutting‑edge technologies.