Due Diligence Basic On AI Analysis
-
-
InfoDetail_Editor: Tony
-
3467
- Wx Share
-
-
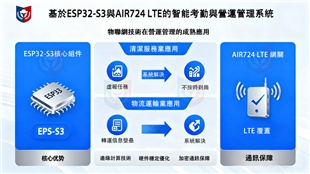
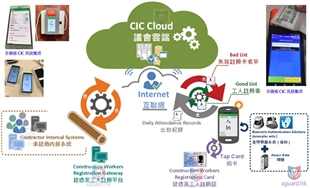
Data integration and AI analysis framework
-

Time & Payroll Suite
Attendance, Payroll and Access Control Solution for Cost Reduction and Productivity Gains Details
All‑in‑one automated timekeeping and payroll system with robust, secure processes to guarantee payroll integrity. Includes leave management, shift rostering, multi‑site and chain support, multi‑ledger accounting, and comprehensive modules.
Due Diligence Basics on AI Analysis

Market Name: AI Due Diligence
Intelligent Early Warning System for Companies and Organizations
Due Diligence Based on AI Analysis
A comprehensive overview and application of the advanced cognitive capabilities and data analysis capabilities of HRMS systems.
Great! Integrating AI due diligence into HRMS systems is a cutting-edge and highly valuable application. The attendance, payroll, and expense data available in the DGX HRMS system is a valuable resource for in-depth employee behavior analysis and risk insights.
Below, I'll build a complete AI due diligence solution for you.
Core Objective: AI Due Diligence System
Due Diligence, in this context, aims to leverage AI models (such as the DeepSeek API) to automatically and intelligently analyze employee behavior data, identify potential risks, unusual patterns, and compliance issues, and provide management with data-driven decision support.
Key Analysis Dimensions:
- Compliance Risk: Examining whether employee behavior complies with company policies, laws, and regulations.
- Financial Risk: Detecting potential fraud, waste, or abuse.
- Operational Efficiency: Assessing employee productivity and cost-effectiveness.
- Turning and Engagement Risk: Predicting the likelihood of high-performing employees leaving.
Data Integration and AI Analysis Framework
The following is a specific plan for leveraging existing data for analysis:
| Data Source | Analyzable Due Diligence Items | How AI Can Help |
|---|---|---|
| Attendance Data | "Ghost Employee" Detection, Absence Patterns, and Overtime Abuse | Analyze clock-in geolocation, IP address, and time patterns to identify clock-in records that have never been linked to critical systems. Build a model to detect unusual overtime patterns (e.g., regular overtime immediately after reimbursement approval). |
| Salary Records | Salary Fairness Analysis and Abnormal Adjustments | Analyze the salary distribution of employees in the same position and level to identify outliers (excessively high or low) that significantly deviate from the group. Monitor salary adjustments that are not processed through normal procedures. |
| Employee Expense Reimbursements | Fake Reimbursements and Policy Compliance | **This is a prime use case for AI analysis! ** Identify unusual invoices (e.g., consecutive invoice numbers, fraudulent merchants), unusual consumption times and locations (e.g., hotel expenses outside of business trips), and duplicate reimbursements. |
| Multi-data Source Correlation | Complex Fraud Chain Detection | Core Value: Correlating expense, attendance, and project data. For example, an employee submitted a travel claim for a certain day, but the attendance record shows they were clocking in at the office that day. Or, a team leader frequently approves unusual reimbursements from a subordinate. |
Provide a new data entry
New Core: Due Diligence Dimension Based on Interaction and Text
Traditional financial audits are "looking back," while your proposed approach is "looking forward" and "getting to the heart of the matter," aiming to assess employee engagement, integrity, cultural fit, and potential behavioral risks.
Dimension One: AI Analysis of Work Reports and Interactions
This component aims to assess work authenticity, productivity, management relationships, and potential warning signs by analyzing textual interactions between employees and supervisors.
| Analysis Objectives | Available Data Sources | AI Analysis Methods and Dimensions |
|---|---|---|
| Work Content Authenticity & Progress Conformity | Employee Weekly/Monthly Reports, Project Progress Reports, Supervisor's Comments | 1. Inter-Period Consistency Analysis: Comparing the employee's progress reported this week with last week, the AI determines whether the progress is reasonable and whether there are any contradictions or ambiguities (e.g., "80% completed" last week, but "started over" this week). 2. Specificity of Outcome Analysis: The AI assesses the quantification and specificity of the work description (e.g., "Completed development of the customer module" vs. "Wrote 5,000 lines of code for the customer module, including 5 API interfaces"). The latter is generally more credible. |
| Employee-Supervisor Relationship & Management Effectiveness | Supervisor's comments, two-way feedback, and one-on-one meeting minutes (if available) | 1. Sentiment and Tone Analysis: Analyze whether the supervisor's comments are positive encouragement ("Great job!"), neutral guidance ("Please complete it by next Thursday"), or negative criticism ("Why are you late again?"). Long-term tracking can reveal changes in the relationship. 2. Feedback Quality Analysis: Evaluate whether the supervisor's feedback is specific and provides actionable guidance. This is also due diligence on the manager. |
| Value Contribution and Strategic Alignment | Work Report Content, Project Descriptions | 1. Topic Modeling and Keyword Extraction: AI automatically identifies the core areas of the employee's work (e.g., is the focus on "customer support" or "technical debt"?). 2. Alignment with Company/Department Goals: Match the report content with the company's quarterly goal keywords to analyze whether the employee's work aligns with the core strategic direction. |
| Resignation and Work Attack Risk Prediction | Report Submission Time, Content Changes, and Language Style Changes | 1. Detecting Behavioral Pattern Changes: An employee who previously submitted detailed and timely reports begins to procrastinate and write perfunctorily. This is a strong risk signal. 2. Language Positivity Analysis: Positive words ("challenge," "accomplished," "learning") decrease in reports, while negative or vague words ("try," "possible," "problem") increase. |
Technical Implementation (DeepSeek API Example):
# Prompt Example: Analyzing a Single Work Report
prompt = f"""
You are a senior HR analyst. Please conduct an in-depth analysis of the following employee's work report:
[Employee Weekly Report]
{weekly_report_text}
[Manager's Feedback]
{manager_feedback_text}
[Employee Last Weekly Report]
{last_weekly_report_text}
Please provide analysis based on the following dimensions:
1. **Progress Alignment**: Did this week's work make reasonable progress based on last week's plan? Are there any inconsistencies or ambiguities?
2. **Outcome Specificity**: Was the description of the work results specific and measurable?
3. **Interaction Quality**: Based on the manager's feedback, analyze the effectiveness of the interaction between the two parties.
4. **Risk Identification**: List one or two of the greatest potential risk points (if any).
Please output in JSON format, including the "score" (percentile) and "analysis" fields.
""
Dimension 2: Social Conduct and Whistleblowing Investigation Analysis
Social Conduct and Whistleblowing Investigation Analysis
This section aims to structure informal, online information so it can serve as supporting evidence for investigations. However, care must be taken to comply with privacy and labor laws.
| Analysis Objectives | Available Data Sources | AI Analysis Methods and Dimensions |
|---|---|---|
| Report Information Integration and Credibility Assessment | Content from anonymous reporting platforms, complaint snippets from internal communication tools (such as Teams/Slack), and publicly available social media information (requires compliance collection) | 1. Entity Recognition: Extract key elements from the text: Person (who), Event (what was done), Time (when), Location (where). 2. Sentiment and Severity Analysis: Determine the emotional intensity of the report (anger, dissatisfaction) and the severity of the accusation (corruption, harassment, work slacking). 3. Multi-Source Information Cross-Verification: AI correlates the report with known data. For example, if a report states that "an employee frequently entertains outside," the report's expense records and attendance records from the same time period can be cross-checked to see if there is supporting or contradictory evidence. |
| Public Opinion Trend Monitoring | (Limited to internal company forums or approved channels) | Topic Monitoring: Monitor internal company communities to see if multiple employees are discussing negative behavior of a specific employee or manager, potentially forming a trend. |
Technical Implementation (Disciplinary Analysis Example):
# Prompt Example: Analyzing a Single Report
prompt = f"""
You are a compliance investigator. Please analyze the following report:
[Report Content]
{whistleblowing_text}
[Related Data Context] (Optional)
- Related Employee Expense Records: {expense_data}
- Related Employee Attendance Records: {attendance_data}
Please complete the following tasks:
1. **Information Extraction**: List the core facts alleged in the report.
2. **Severity Assessment**: Classify the allegations as "high risk" (e.g., illegality, fraud), "medium risk" (e.g., policy violation), or "low risk" (e.g., interpersonal conflict).
3. **Preliminary Credibility Assessment**: Determine the credibility of the report (high, medium, or low) based on the specific details and context provided (if any).
4. **Investigation Recommendations**: Recommends next steps for investigation (e.g., "Review surveillance during the XX time period," "Interview XX relevant individuals").
Output format is JSON.
""
Integrated Due Diligence Report: Final AI Output
The ultimate value of AI isn't providing discrete insights, but rather generating a Integrated Due Diligence Report. This report can be generated for a single employee or a team.
Report structure example:
{
"employee_id": "12345",
"risk_score": 65,
"risk_level": "Medium",
"summary": "This employee's financial data is normal, but work reports show slow progress and negative interactions with their supervisor. There is a recent anonymous report that requires attention."
"details": {
"financial_analysis": {...},
"work_report_analysis": {
"consistency_score": 40,
"specificity_score": 30,
"manager_engagement_trend": "Declining",
"key_risk": "Failed to meet self-imposed milestones for two consecutive weeks and did not respond to supervisor's guidance feedback."
},
"conduct_analysis": {
"reported_incidents": 1,
"latest_incident": {
"severity": "Medium",
"credibility": "Medium",
"summary": "Reported for using company resources for personal matters.",
"recommended_action": "It is recommended to review the network and device usage logs with the IT department. "
}
}
},
"recommended_actions": [
"1. The supervisor should conduct a formal interview with the employee to understand the obstacles to project progress. ",
"2. The Compliance Department should initiate a preliminary investigation into the report. "
]
}
Technical Implementation Path (How to Do It)
Step 1: Data Preparation and Preprocessing
- Data Cleansing and Standardization: Clean data from different DGX HRMS modules (CSV, database tables), unifying time formats, currency units, employee IDs, etc.
- Feature Engineering: This is the most critical step. Convert raw data into features that the AI model can understand.
- Attendance Features: Monthly number of latenesses and early departures, average daily work hours, frequency of weekend overtime, frequency of IP address changes when clocking in, etc.
- Reimbursement Features: Monthly total reimbursement amount, reimbursement frequency, average single reimbursement amount, proportion of each category for food, transportation, and accommodation, invoice number consistency, etc.
- Salary Features: Deviation from department average salary, historical salary increase range, correlation between bonuses and performance, etc.
- Data Anonymization: For privacy reasons, hashed employee IDs can be used instead of real names during training and analysis.
Step 2: Model Selection and Analysis
For Quantitative Anomaly Detection (Best Path):
- Using a Machine Learning Library (e.g., Scikit-learn): Run the model directly on your server for low cost, high speed, and good privacy protection.
- Isolation Forest and One-Class Support Vector Machine (SVM): Well-suited for identifying a few "anomalies" from the majority of "normal" behavior.
- Logistic Regression/Decision Tree: Used for classification of labeled data (e.g., training a model to predict new cases given a known set of historical fraud cases).
- Process: Extract features using Python -> Use the trained model for predictions -> Output anomaly scores and labels.
**For Qualitative Analysis and Deep Insight (with API):
Using the DeepSeek API: Used when understanding complex context and generating natural language reports are required.
Scenario: Send all data (features, raw records) for an employee marked as "abnormal" to DeepSeek, requesting it to analyze risk points and generate an easy-to-understand investigation summary for HR.
Sample prompt:
"You are an HR investigation expert. Please analyze the following employee's data, identify potential compliance risks, and provide investigation recommendations in a concise list format." [Employee ID]: 12345 [Abnormal Features]: Employees whose monthly expense total exceeds 98% of the department's total, frequently claiming meals during off-hours, and whose invoice numbers are multiple and consecutive. [Raw Data Snippet]: [Insert a few sample expense records here] Please analyze: Do these actions potentially constitute fraudulent expense claims? What should the investigator focus on next? ”
Step 3: System Integration and Deployment
Batch Processing Mode: Automatically run the anomaly detection model weekly or monthly, scanning all employee data and generating a "Risk Employee Ranking" report.
Real-Time API Mode: Within the HRMS system, when a manager submits a reimbursement request for approval, the model is invoked in real time to perform a risk score and provide a prompt on the approval screen (e.g., "This request has unusual characteristics; please proceed with caution").
Visual Dashboard: Create a management view displaying key risk indicators, trend charts, and detailed alert lists.
Why is this a better solution?
Privacy and Cost: Core anomaly detection is performed locally, avoiding the frequent sending of sensitive data to an external API.
Efficiency: Machine learning models process numerical features extremely quickly, making them suitable for large-scale screening.
Accuracy: AI models can detect complex patterns and multivariate correlations that are imperceptible to the human eye.
Interpretability: Using DeepSeek APIs provide human-friendly explanations for anomalies generated by "black box" models, closing the loop.
Action Plan Recommendations
Start Small: Select a risk scenario to pilot, such as "employee expense fraud detection."
Build a Team: This requires collaborative work between data engineers (to process the data), machine learning engineers (to build the model), and HR business experts (to define the rules and interpret the results).
Proof of Concept (PoC): Train a simple isolation forest model on historical data to see if it can successfully identify known anomalies.
Iterative Optimization: Gradually increase the complexity of the data source and model, ultimately integrating it into the DGX HRMS process.
With this approach, your HRMS system will transform from a system of record into a powerful risk insight and decision support system – the disruptive value of AI.
Software Service
Industry information
- Views 8944
- Author :Tony
- Views 603
- Author :Tony
- Views 1661
- Author :Bruce Lee
- Views 41
- Author :Tony
- Views 15
- Author :Bruce Lee
- Views 29
- Author :Tony
































































Hardware & Software Support
We are deeply rooted in Hong Kong’s local services, specializing in hardware and software issues.
System Integration
Hardware and software system integration to enhance stability and reliability.
Technical Support
Professional technical team providing support.
Professional Technical Services
Focused on solving problems with cutting‑edge technologies.